Research: Solid Particle-laden Flows
Gas-solid Risers
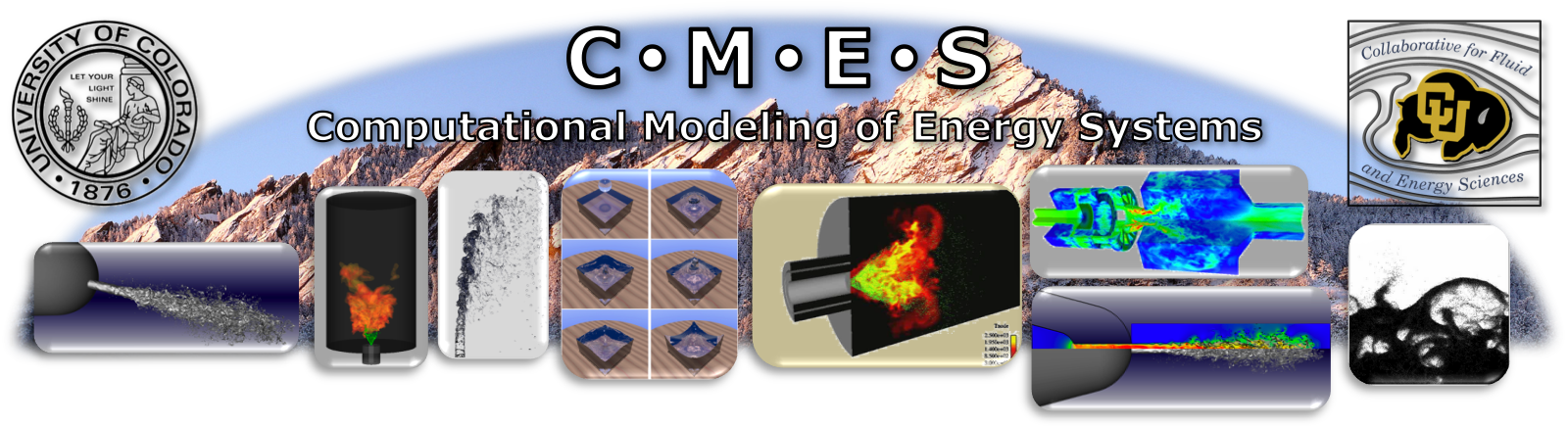
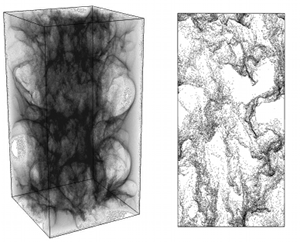
Gas-particle flows in vertical risers are used in many industries including gasification/pyrolysis for biofuel conversion, coal combustion, and fluid catalytic cracking. Experimental studies have shown riser flows to be unsteady with large solid-volume fraction fluctuations. Regions of densely-packed particles, referred to as clusters and streamers form, which greatly affect the overall flow behavior and mixing properties. A Eulerian-Lagrangian approach is used to simulate riser flows and better understand the cluster formation. The gas phase is solved on an Eulerian grid while each particle is tracked individually.
The first image shows a 3D simulation of the flow destabilizing (10.2 million particles, Re=1, Fr=55.5), along with a 2D cross section of the flow at a later time to convey particle clustering. The simulation was conducted on 4 million grid points using 512 processors for approximately one week. The second image shows instantaneous gas volume fraction of the flow with and without collisions.